Hyperkalemia is not always expressed with EKG changes. Hyperkalaemia causes a rapid reduction in resting membrane potential leading to increased cardiac depolarization and muscle excitability which in turn causes EG changes 1.
ECG changes have a sequential progression which roughly correlate with the potassium level but with the caveats mentioned above 2 Early ECG changes of hyperkalemia typically seen at a serum.
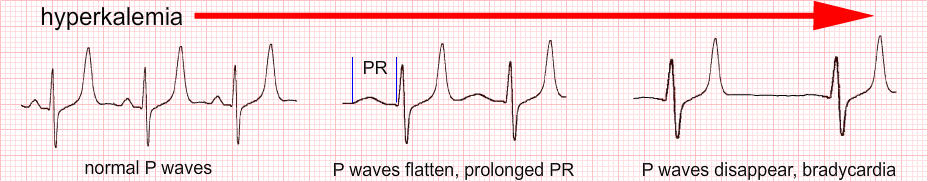
Ecg changes in hyperkalemia. In a prospective series 46 of patients with hyperkalemia were noted to have electrocardiographic changes but no clear criteria were presented. Recognition of the ECGEKG changes of hyperkalemia can save lives. In most cases EKG changes have good correlation with the degree of hyperkalemia.
But the levels at which ECG changes are seen are quite variable from person to person. Any acute or chronic kidney disease or dysfunction interrupts the delicate homeostasis and causes hyperkalemia. Kayexalate takes time to work.
With severe hyperkalemia effect on RMP becomes prominent. IV insulin f ollowed by glucose will shift potassium intracellularly and is an effective treatment for severe hyperkalemia. Minimal potassium level 55 to 65 mEqL.
Design setting participants measurements. In patients with mild hyperkalemia potassium conductance IKr through potassium channels is increased which tend to shorten the AP duration and on the ECG causing tall tented T waves. Pt with ESRD getting dialysis 3 times per week presents with K 9 on.
The effect is transient but the calcium injection can be repeated until measures to correct the hyperkalemia are undertaken. It produces predictable changes on the ECGEKG. There is a predictable EKG progression as the serum potassium becomes more elevated.
Electrocardiogram Findings in Hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia serum K 55 mmoll is a life-threatening medical emergency. Hyperkalemia causes a rapid reduction in resting membrane potential leading to increased cardiac depolarization and muscle excitability.
Classic teaching of the chronological ECG changes of hyperkalemia include. ECG findings in hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia can result in a variety of presentationsincluding asymptomatic dyspnea nauseavomiting diarrhea weakness chest pain missed dialysis or cardiac arrest. Prolongation of PR interval.
12 Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum level of potassium greater than 55 mEqL. Potassium of 7 is severe hyperkalemia. Where did the evidence for order of ECG changes of hyperkalemia come from.
Charts were reviewed for patients who were admitted to a community-based hospital with a diagnosis of hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia serum K 55 mmoll is a life-threatening medical emergency. Most patients have risk factors including CKD CHF DM or medications like ACE inhibitors or potassium-sparing diuretics.
It produces predictable changes on the ECGEKG. Recognition of the ECGEKG changes of hyperkalemia can save lives. Tall peaked tented T waves T wave larger than R wave in more than 1 lead.
Loss of P wave Sine Wave Asystole. The electrocardiographic ECG or EKG changes with hyperkalemia do not consistently follow a stepwise dose-dependent pattern. There are five ECGEKG changesgroups of changes associated with hyperkalemia which you must be able to recognise.
Peaked T waves usually the earliest sign of hyperkalaemia. Although the electrocardiogram ECG is not considered a reliable indicator of mild to moderate hyperkalemia profound elevations of serum potassium concentration generally produce classic ECG manifestations. You want to urgently bring down the potassium.
There are five ECGEKG changesgroups of changes associated with hyperkalemia which you must be able to rec. ECG changes are usually progressive and may include. Hyperkalemia with ECG changes.
It produces predictable changes on the ECGEKG. Electrophysiologic basis of ECG changes. It can be further broken down as follows.
Associated with minor ECG changes. We report two cases of severe hyperkalemia 90 mEqL in which the ECGs did not reveal the expected manifestations of hyperkalemia. Hyperkalemia serum K 55 mmoll is a life-threatening medical emergency.
As the severity of hyperkalemia increases the QRS complex widens and the merging together of the widened QRS complex with the T wave produces the sine wave pattern of severe hyperkalemia. Tall tented T waves. In this one critical minute we talk about the ECG changes in hyperkalemiaThe first changes that occur as potassium levels rise are the peaking of T-waves.
This in turn can cause electrocardiographic ECG or EKG changes 10. In the presence of ECG changes and hyperkalemia intravenous calcium usually as gluconate since chloride is chemically more toxic if extravasated results prompt reversal of ECG changes. Effects of hyperkalaemia on the ECG Serum potassium 55 mEqL is associated with repolarization abnormalities.
EKG changes also depend on the rate of increase in potassium concentration. Recognition of the ECGEKG changes of hyperkalemia can save lives.
