AP view right knee421. The main tendon found at the knee is the patellar tendon which links the quads muscles to the shin bone.
As the knee is a synovial hinge joint its function is to permit the flexion and extension of the lower leg relative to the thigh.

Anatomy of a knee. Fast facts on knee anatomy The knee is the largest and most complex joint in the body. Intro to knee x-rays014. The primary movements at the knee joint include flexion and extension with limited internal and external rotation.
Tibiofemoral medial and lateral condyles of the femur articulate with the tibial condyles. The knee joint is a complex structure that involves bones tendons ligaments muscles and other structures for normal function. The lateral and medial femorotibial articulations between the lateral and the medial condyles of the femur and tibia as well as the intermediate femoropatellar articulation between the patella and the femur.
The knee is a modified hinge joint which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis. Identify bony and soft tissue structures of the knee by visually assisted and self-guided palpation.
Normal Anatomy and Biomechanics of the Knee Fred Flandry MD FACSw and Gabriel Hommel MD Abstract. The smaller bone that runs alongside the tibia fibula and the. To measure the extent of internal and external rotation the knee must therefore be flexed to a right angle.
Sec-ondary movement internal and external rotations of the tibia in relation to the femur is possible only when the knee is flexed. These syndromes a. The knee joint has three main articular areas.
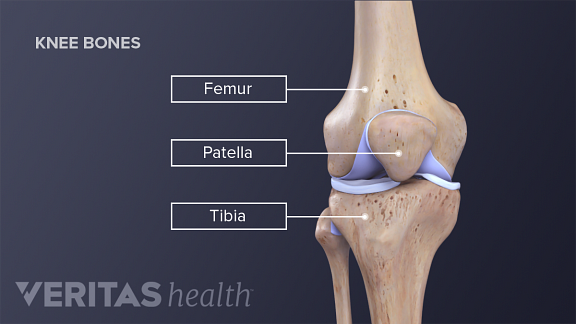
The knee joins the thigh bone femur to the shin bone tibia. In humans and other primates the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints. As a hinged joint the knee joint mostly allows movement along one axis in terms of flexion and extension of the knee in the sagittal plane.
Identify locations of bony landmarks on the knee. Between the medial condyle of the femur the medial condyle of the tibia. One between the femur and tibia and one between the femur and patella.
There are two main joints in the knee. The range of motion of the knee is limited by the anatomy of the bones and ligaments but allows around 120 degrees of flexion. Clinical anatomy of the knee The clinical anatomy of several pain syndromes of the knee is herein discussed.
This video tutorial presents the anatomy of knee x-rays000. It is made up of two joints the tibiofemoral joint between the tibia and the femur and the patellofemoral joint between the patella and the femur. The knee is a complex joint that flexes extends and twists slightly from side to side.
Knee Anatomy - The Knee Joint is the largest complex joint in the body. Identify common muscles and tendons of the knee. The knee is the meeting point of the femur thigh bone in the upper leg and the tibia shinbone in the.
2 Latral Condylar Joint. 1 the tibiofemoral joint where the tibia meet the femur 2 the patellofemoral joint where the kneecap or patella meets the femur. Identify key ligaments and structures of the knee.
1 Medial Condylar Joint. The joint surfaces are lined with hyaline cartilage and are enclosed within a single joint cavity. The main movement of the knee is flexionextension.
The joint is stabilised by several of ligaments. Ebraheims educational animated video describes the anatomical structures of the knee in a very simple and easy wayBony structures of the kneeFemurPat. It also allows slight medial rotation during flexion and the last stage of extension of the knee as well as lateral rotation when unlocking the knee.
The knee joins together the thigh bone shin bone fibula on the outer side of the shin and kneecap. Notice that the fibula does not participate in the knee joint. They are they soft tissues found at the end of muscles which link the muscle to bone.
When there is damage to one of the structures that surround the knee joint this can lead to discomfort and disability. The knee is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. Between the lateral condyle of the femur the lateral condyle of the tibia.
- It consists of 3 Joints. The knee cap actually sits inside the patellar tendon. Explore overall anatomy of the knee including muscles bones ligaments and motions.
The knee joint is a synovial joint which connects the femur thigh bone the longest bone in the body to the tibia shin bone. Stability of the joint is governed by a combination of static ligaments dynamic muscular forces meniscocapsular aponeurosis bony topography and joint load. It is often termed a compound joint having tibiofemoral and patellofemoral components.
These include the iliotibial tract syndrome the anserine syndrome bursitis of the medial collateral ligament Bakers cyst popliteus tendon tenosynovitis and bursitis of the deep infrapatellar bursa. Tendons are often overlooked as part of knee joint anatomy. Functionally the knee comprises 2 articulationsthe patellofemoral and tibiofemoral.
Standard knee series for x-rays021. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee joint consists of two articulations tibiofemoral and patellofemoral.