Specific Heat Capacity does not depend on mass of. In thermodynamics the specific heat capacity symbol c p of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample.
Specific heat or specific heat capacity s is the heat capacity which is independent of the amount of substances.
Heat capacity vs specific heat. Specific Heat Capacity definition. Heat Capacity of the substance is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the substance by 1 o C whereas Specific Heat Capacity is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature by 1 o C of unit mass of substance. 3Specific heat is more suitable for use in theoretical and experimental functions.
A more meaningful material property is the. Find the adequate equation for your fluid. Table 6 Thermal Conductivity Specific Heat Capacity and Density System Material Database Material Description.
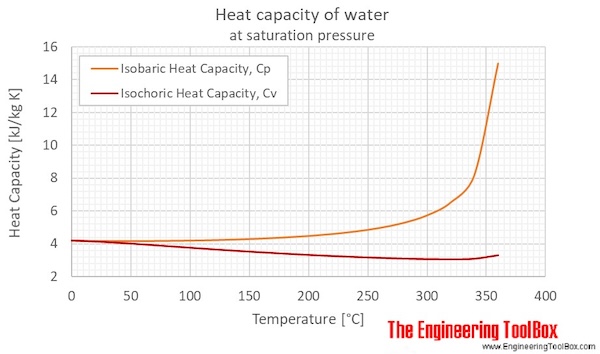
Water - Specific Heat - Online calculator figures and tables showing specific heat of liquid water at constant volume or constant pressure at temperatures from 0 to 360 C 32-700 F - SI and Imperial units. Two difference between Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Capacity are. Generally the most constant parameter is notably the volumetric heat capacity at least for solids which is notably around the value of 3 megajoule per cubic meter and kelvin.
The measured heat capacity depends on the sample size and does not characterize the material. Informally it is the amount of energy that must be added in the form of heat to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperatureThe SI unit of specific heat is joule per kelvin and kilogram. Specific heat capacity C is defined as the amount of heat absorbed Q in order to increase the temperature T by 1 unit of a unit massm.
Since temperature is something like the averaged kinetic energy the heat capacity loosely counts the number of degrees of freedom in the atom heat is randomized kinetic energy that needs to be transfered to the material. The main difference between specific heat and heat capacity is that specific heat is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a given sample by 1 K while heat capacity is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of substance by 1 K. That is C Q 4T.
It can be defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius or one Kelvin at a constant pressure. For DSC measurements the heat capacity is essentially the ratio of the heat flow and the heating rate. You can relate them by temperature Cite.
Density WmK JkgK kgm3 Asphalts Other Roofing Finishes Asbestos Cement Decking. The specific heat for some commonly used liquids and fluids is given in the table below. Heat capacity is dependent on the amount of substance.
Specific heat and heat capacity both describe an amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance. 2Specific heat has a unit of mass in its equation as recommended by the International Standards of measurement. 1Heat capacity is an extensive variable while specific heat is an intensive variable.
Heat capacity Hc is defined as the amount of heat absorbed Q in order to increase the temperature T by 1 unit. Heat Capacity Speciflc Heat and Enthalpy Stephen R. Specific heat capacity and viscosity are mostly functions of temperature.
Units of Heat - BTU Calorie and Joule - The most common units of heat are BTU - British Thermal Unit Calorie and Joule. The basic difference between specific heat and heat capacity is that specific heat is the heat that must be supplied to the unit of mass of a given substance to raise its temperature by one degree and it is an intensive property and the heat capacity depends on the amount of matter considered therefore it is extensive. The unit of the heat capacity C p is Joules per Kelvin.
Heat Capacity vs Specific Heat Capacity. Heat Capacity is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a substance to 1 degree Celsius C or 1 Kelvin whereas specific heat is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of substance having mass 1kg or 1g by 1 degree Celsius C or 1 Kelvin. Asbestos Cement Sheet.
The key difference between heat capacity and specific heat is that heat capacity is dependent on the amount of substance while specific heat capacity is independent of it. For conversion of units use the Specific heat online unit converter. More degrees of freedom higher heat capacity.
See also tabulated values of specific heat of gases food and foodstuff metals and semimetals common solids and other common substances as well as values of molar specific heat of common organic substances and inorganic substances. Addison January 22 2001 Introduction In this section we will explore the relationships between heat capacities and speciflc heats and internal energy and enthalpy. Heat Capacity The heat capacity of an object is the energy transfer by heating per unit tem-perature change.
The following table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials and when applicable the molar heat capacity. The more degrees of freedom the less energy every degree needs to take on when energy transfered to the material ie. Furthermore when considering the theory the heat capacity of the amount of heat needed to change a substances temperature by 1C or 1K while specific heat is the heat needed to change 1g of substances temperature by 1C or 1K.