Coats disease is a form of retinal telangiectasia with lipid-rich subretinal exudates. Coats disease is a rare congenital nonhereditary eye disorder causing full or partial blindness characterized by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina.
 Figure 1 From Coats Disease Of Adult Onset Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Coats Disease Of Adult Onset Semantic Scholar
Whereas simple Coats disease almost exclusively occurs unilaterally and in males both sexes and both eyes may have Coats retinal lesions in this syndrome.
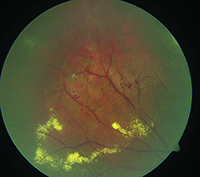
Coats disease in adults. What causes Coats Disease. 1 The mainstay of management of Coats disease is photocoagulation to treat the nonperfused retina and to obliterate the aneurysms and leaking vessels. Coats disease is an eye disorder characterized by abnormal development of the blood vessels in the retina retinal telangiectasia.
When this entity appears in adults it usually exhibits a more benign clinical course. Coats disease lesions may also occur in Labrune syndrome 614561 and of course in isolation. It most often appears at 8-10 years of age affects males three times more often than females and usually affects only one eye.
The majority of Coats disease is diagnosed between ages 8 and 16. Coats disease can also fall under glaucoma. 8 This contrasted with the Shields series in childhood Coats where macroaneurysms with retinal hemorrhages were only present in 13 of cases.
Coats disease also known as exudative retinitis is an uncommon eye condition that affects the smaller blood vessels capillaries found in the retina. Coats disease is a rare condition in which abnormal blood vessels in the retina dilate and leak fluid resulting in damage to the retina and possibly vision loss. Early signs and symptoms vary but may include vision loss crossed eyes strabismus and a white mass in the pupil behind the lens of the eye leukocoria.
Four of our patients did develop exudative RDs but these detachments responded well to laser treatment and no patient developed neovascular glaucoma. Coats disease is an idiopathic condition characterized by retinal telangiectasia with intra- and subretinal exudation leading to exudative retinal detachment without any signs of vitreoretinal traction. It usually occurs in males between 4 and 10 years of age and is unilateral in 80 of cases.
In a series of adult-onset Coats disease 77 of cases demonstrated arterial macroaneurysms associated with intraretinal hemorrhages suggestive of prior rupture. Its more frequent in males at least 31 than females and in patients younger than 8 years old even though it has been observed in infants as well as older patients. 1 Alternative diagnoses should especially be considered in female adult-onset or bilateral cases.
It is a rare condition affecting 1 in 100000 people. It is mainly a disease of childhood and only on rare occasions has it been described in adults. Coats disease is a rare eye disorder involving abnormal development of blood vessels in the retina.
In adults it typically has a more insidious clinical course. Located in the back of the eye the retina sends light images to the brain and is essential to. 12 Anti-VEGF injections and periocular.
Most people begin showing symptoms in childhood. It can have a similar presentation to that of retinoblastoma. Coats disease can make these blood vessels weak and grow incorrectly causing them to leak fluid and blood under the retina.
The retina is the light-sensitive layer that lines the inside of your eye. Adult-onset Coats disease has less extensive involvement more benign natural course and a more favorable treatment outcome as against the childhood-onset disease. Coats disease is a retinal vascular abnormality characterized by idiopathic retinal vascular telangiectasia and microvascular aneurysmal changes that can cause exudation and exudative retinal detachment.
Coats disease is usually characterized by unilateral 95 progressive development of abnormal vessels in the retina of the affected individuals. The vast majority of Coats disease is diagnosed in the first decade of life although mild forms of the condition can present well into adulthood45 The disease occurs sporadically and no hereditary pattern has been identified despite reports that individual cases of Coats disease have occurred as a result of localized mutations in proteins governing angiogenesis6 More than 75 percent of. Diagnosis of this condition must be.
1 There are reports of cases presenting in adulthood but this is less common. Coats disease is much more common in males than females. It is most commonly discovered in children before the age of 10 years but can present in adulthood too.
Most cases of Coats disease are diagnosed in childhood. Coats disease in adults seems to advance at a slower rate than it does in children with the majority of patients reaching a stable final VA. 78 Greater than 75 percent of patients are male and 95 percent of cases are unilateral.
Coats disease diagnosed in adulthood is an idiopathic retinal exudative vascular disease without an inciting factor and has retinal features different from the childhood disease.
Ischemic white matter disease refers to small blood vessels in the brain that are clogging up a bit. White matter disease or leukoaraiosis involves the degeneration of the brains white matter.
 Cerebral Small Vessel Disease From Pathogenesis And Clinical Characteristics To Therapeutic Challenges The Lancet Neurology
Cerebral Small Vessel Disease From Pathogenesis And Clinical Characteristics To Therapeutic Challenges The Lancet Neurology
This misnomer comes from health practitioners referring to it as such but periventricular white matter is commonly occurring on the brain and changes in this matter are common as people age 1.

Microvascular ischemic white matter disease. In this MRI of the brain there are multiple white spots that appear very brightly in the brain tissue. White matter disease usually occurs due to aging but it can also affect young people. 16 years experience Neurology.
White matter is the part of the brain where the communication cables are and t. Ischemic changes are areas in the brain tissue that have died from lack of blood flow. This is usually not a serious condition unless the amount of small vessel disease gets to a moderate or severe degree.
Microvascular ischemic white matter disease is a general description pointing out to problems with the blood vessels supplying certain areas of the brain. White matter distress is a progressive condition caused by an age-related decline in the part of the nerves the white matter that connect different areas of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord. It is only when a person undergoes a scam that microvascular ischemic disease is accidentally discovered.
Lesions which are identified through imaging may lead to a disconnect between certain regions of the brain thereby creating. Changes to these vessels can damage white matter the brain tissue. Tonight almost a year later I happened to find that report.
White matter disease is the wearing away of tissue in the largest and deepest part of your brain that has a number of causes including aging. If the patient is given and infusion of gadolinium the spots will appear even brighter on the MRI film. It was first proposed by Vladimir Hachinski fl 2019 a Ukrainian-born Canadian neurologist 6.
The differential diagnosis is wide and includes multiple diseases involving the white matter including. These are signs of microvascular ischemic disease in the brain tissue. It is often caused by high blood pressure diabetes high cholesterol or smoking.
Chronic microvascular ischemic changes in the brain are often picked up incidentally on a scan of the brain most typically an MRI. This happens over time due to changes in the blood vessels or blood clots. Low attenuation in periventricular white matter consistent with chronic small vessel ischemic disease.
Understanding the causes symptoms and treatment options is important since it is one of the major causes of death worldwide. These nerves are also called white matter. What they are is small areas in the brain where tiny blood vessels have ruptured or clotted off causing essentially extremely small areas of strokes.
A person with strong immune system can have microvascular ischemic disease without demonstrating any symptoms. Chronic means this process has been going on for years in the brain. Microvascular disease is caused by age-related changes in the brain and has also been linked to hypertension.
16 years experience Neurology. What Is Chronic Microvascular Ischemic Disease. The term leukoaraiosis means white matter rarefaction and comes from the Greek leuko white and araios rarefaction.
What is chronic periventricular white matter microvascular ischemic disease. Problems with blood supply to certain parts would manifest as these white spots in the brain parenchyma or white matter. Periventricular White Matter Disease is not actually a disease.
Diagnosing microvascular ischemic white matter disease. This condition can result in imbalance a. Chronic means this process has been going on for years in the brain.
What is chronic periventricular white matter microvascular ischemic disease. This tissue contains millions of nerve fibers or. White matter is the part of the brain where the communication cables are and t.
Microvascular ischemic disease is a term thats used to describe changes to the small blood vessels in the brain. It is more common to be seen the older you get. Microvascular ischemic disease sounds ominous and it can be.
This concerned me because recently I was hospitalized following a traumatic fall. It is the result of blockage to the small blood vessels in the brain. The effects of diseased brain arterioles show up in imaging studies as subcortical lesions as well as in strokes caused by the blockage of the small blood vessels that go deep into the brain in microbleeds and in white matter lesions according to NIH.
White matter disease is a disease that affects the nerves that link various parts of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord. Microvascular ischemic disease affects tiny blood vessels that are less than 05 millimeters mm in diameter which makes the condition challenging to identify and treat with surgical procedures. Most of the time the condition is undiagnosed.
Due to a number of falls in 2016 I had a CT brainhead wo contrast scan.
Widespread scarring and obliteration of the bronchioles results in the indirect sign of patchy density differences of the lung parenchyma representing areas of under-ventilated and under-perfused lung the so-called mosaic attenuation pattern. Hogg and colleagues 21 in 1968 first used the term small airways disease to describe airway disease in patients with variably severe chronic airflow obstruction characterized by loss of bronchioles mucus plugs and variable amounts of inflammation and fibrosis that involve the smallest bronchi as well as the bronchioles so that neither bronchitis nor bronchiolitis is an appropriate term.
 Small Airway Disease Google Search Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Lung Disease Disease
Small Airway Disease Google Search Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Lung Disease Disease
We empower healthcare organizations and physicians to improve patient outcomes streamline care coordination and drive efficiencies.

Small airway lung disease. Small airway disease is defined as a pathologic condition in which the small conducting airways are affected either primarily or in addition to alveolar or interstitial lung changes. Small airways however comprise a substantial component of the conducting lung air flow. Abnormalities on HRCT that reflect small airways disease can be broadly categorized into indirect and direct signs.
For the pathologist small airway disease has the same meaning as bronchiolitis a nonspecific term used to describe inflammation of the membranous and respiratory bronchioles. Bronchiolitis obliterans is the most common disease affecting small airways after lung transplantation. 104120123 There is also inflammation in the smaller bronchi and bronchioles.
This represents a nonspecific reaction to acute lung injury and can be seen in a variety of circumstances. Two Models of Parenchymal Airspace Enlargement in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Airways that are more peripheral to the main bronchi and proximal bronchioles 4 th the 14 th generation - arbitrarily considered to be those with an internal diameter of 2 mm 3.
Small airways disease comprise of a group infectious as well as non-infectious conditions that affect the small airways ie. The pathophysiology in asthma and COPD involves not only the proximal large airways but also. It also occurs in patients with allogeneic but not autogenic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation HSCT.
In Panel A alveolar inflammation leads to the destruction of alveolar walls and the elastic fibers of connective tissue that link the acinus to the terminal airways. Asthma is a long-term lung disease characterizedby inflammation of the lower airwaysand episodes of airflow obstructionAsthma severity ranges from intermittentmild symptoms such as coughs and. Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD are chronic inflammatory disorders of the respiratory tract that are characterized by airflow limitation.
The relative contributions of these two factors vary between people. 118 This takes place at the expense of Clara cells 119 which together with the serous cells of the bronchial glands secrete an airway-specific low-molecular-weight protease inhibitor antileukoprotease which is a potent protective factor against the development of emphysema. Asthma is well recognized as a disease of both large and small airways.
Small airway is considered the primary defect in asthma but one cannot diagnose the presence of asthma by small airway obstruction alone. VIDA helps modernize lung and respiratory care through intelligence. They are distinct conditions with different causes structural changes and immunopathology.
Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia BOOP pattern is characterized by classic bronchiolitis obliterans with intraluminal polyps affecting mainly respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. Most recently indirect evidence of involvement of the small airways in the process of lung ageing has been shown by CT as the degree of functional small airway disease was shown to increase by 27 per decade ranging from 36 4050 years to 127 age. Over time chronic inflammation in this area can cause thickening in these airways and lead to mucus blockages in your.
Small-airway disease is characterised by bronchiolar goblet cell hyperplasia. The presence of abnormally dilated or thick walled airways in the relatively lucent lung confirms underlying airway disease see small airways disease parenchymal changes. The small airways usually defined as those with an internal diameter of 2 mm are recognized as the major site of resistance to airflow in obstructive lung disease.
In asthma inflammatory processes can affect the whole respiratory tract from central to peripheralsmall airways. RA can also lead to inflammation within the small airways of your lungs. The poor airflow is the result of breakdown of lung tissue known as emphysema and small airways disease known as obstructive bronchiolitis.
Crazy paving pattern or nodules. The small airways constitute one of the least understood areas of the lungs. The emphasis in adult and pediatric respiratory disease clinics is to focus on large airway obstruction and reversibility.
They play a role in many lung diseases and small airway pathology results in significant morbidity New approaches to their evaluation may provide insights into this major area of lung disease. COPD is a type of obstructive lung disease in which chronic incompletely reversible poor airflow airflow limitation and inability to breathe out fully air trapping exist. Ground glass opacity is the likely cause for mosaic attenuation if other features of the infiltrative disease are present such as reticular opacities ie.