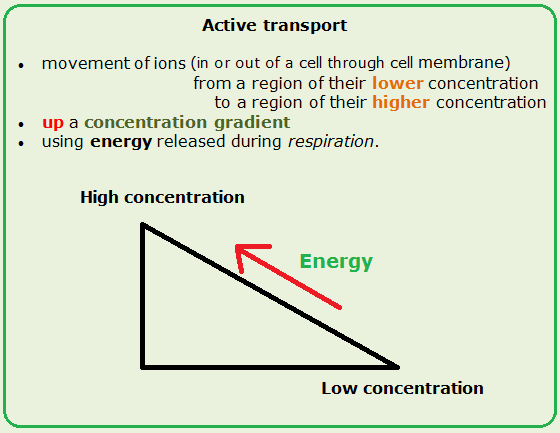
Active Transport requires energy because it is moving molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive changes.
Active Transport Across Cell Membranes
These solutes are unable to cross the membrane by any form of passive transport as they need to move against the concentration gradient so they take the path of active transport.
Active transport definition biology. There are three main types of proteins that engage in active transport. Primary active transport that uses adenosine triphosphate and secondary active transport that uses an electrochemical gradient. Active transport is the process by which materials move from a lower concentration to a higher concentration.
Active transport is the energy-demanding transfer of a substance across a cell membrane againstits concentration gradient ie from lower concentration to higher concentration. Active transport is transport against a concentration gradient that requires chemical energy. Definition Active transport is the process of transferring substances into out of and between cells using energy.
Free learning resources for students covering all major areas of biology. Using adenosine triphosphate ATP needed for cellular energy from respiration molecules can move from one side of a cell wall to anotherKeep reading to find examples of active transports in both plants and animals. Moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient a cell must use energy.
Active transport of ions or molecules is achieved through the use of an integral membrane protein. Active transport mechanisms do just this expending energy often in the form of ATP to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. The movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane in the direction opposite that of diffusion that is from an area of lower concentration to one of higher concentration.
Active transport requires cellular energy to achieve this movement. In some cases the movement of substances Active transport relies on the use of energy to move substances into and out of cells. Active transport in the largest biology dictionary online.
Active transport is a mode of transportation in plants which uses stored energy to move the particles against the concentration gradient. Active transport is the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances eg.
In cellular biology active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentrationagainst the concentration gradient. Active transport is the movement of particles against a concentration gradient from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration at a rate faster than diffusion. It requires the expenditure of energy.
Special proteins within the cell membrane act as specific protein carriers. It requires energy in the form of ATP. Active transport is the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy from respiration Extended Only Examples of Active Transport.
Active transport The movement of dissolved substances across a membrane in the direction opposite to that of normal diffusion. Ions glucose and amino acids are transported across a biological membrane towards the region that already contains a lot of such. An example of active transport in human physiology is the.
In a plant cell it takes place in the root cells by absorbing water and minerals. In several cases however the cell has to transport anything against its concentration gradient. In some cases this could be accomplished through transport that uses no energy.
Campbell Biology by JB. Active transport is a process in which polar or charged solutes are transported across the membrane against the concentration gradient by using energy. Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein using energy supplied by ATP.
Active transport mechanisms collectively called pumps or carrier proteins work against electrochemical gradients. Active transport Definition Transport that moves solutes against their concentration gradients with the help of proteins is called active transport. Active Transport Definition To sustain life several substances have to be compelled to be transported into out of and between cells.
It is a selective process as certain molecules can only be transported by certain proteins. Unlike most forms of passive transport active transport is directional that is it transports a specific substance in only one direction. With the exception of ions small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes.
Active transport always leads to accumulation of molecules are ions towards one side of the membrane. Molecule binds to carrier protein on one side of the membrane. There are two types of active transport.
Active transport operates against gradients of chemical concentration electrical charge or electrochemical state.
For example water as a hydride of oxygen H2O has a higher melting point boiling point heat of vapourization and surface tension than do the comparable hydrides of sulfur H2S and nitrogen NH3 and most other common liquids. A chemical bond in which ions are held together by the attraction between their opposite charges What is an ionic compound.
 Properties Of Water Lab Ap Biology Lab 1 Introduction Water Is A
Properties Of Water Lab Ap Biology Lab 1 Introduction Water Is A
H 2 O What are the two main types of chemical bonds.
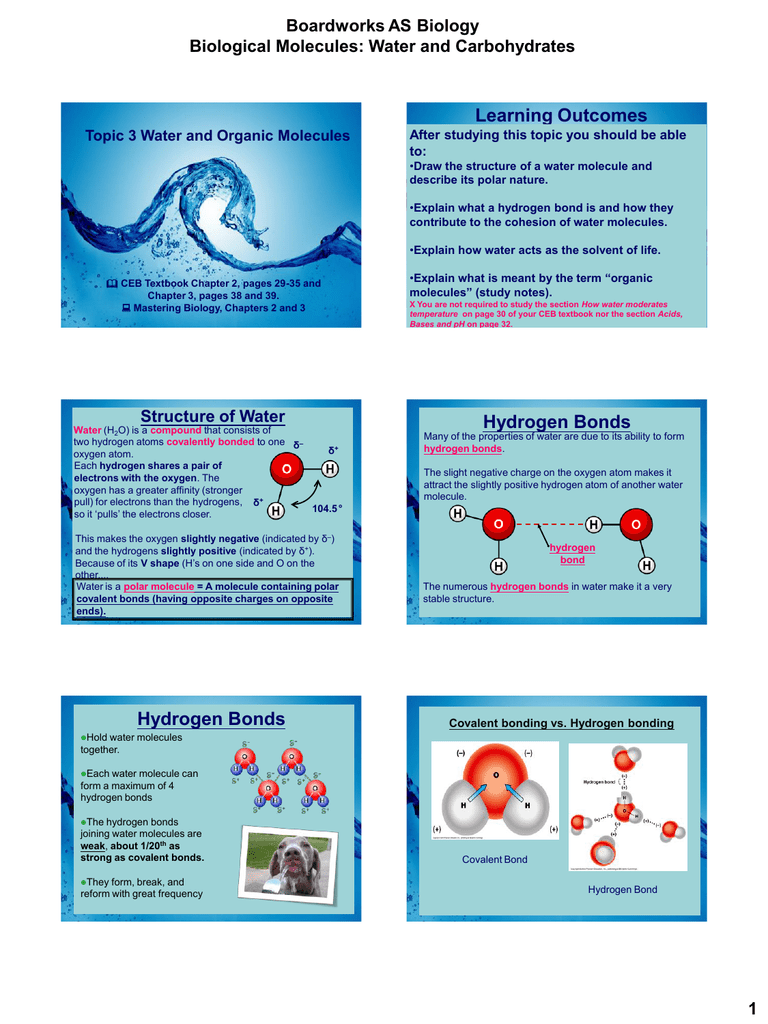
Properties of water biology. Hydrogen Bonding in a Snap. Heat energy can be absorbed by breaking hydrogen bonds Five Critical Properties of Water 3. Water H2 O is a polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid nearly colorless with a hint of blueThis simplest hydrogen chalcogenide is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the universal solvent for its ability to dissolve many substances.
Why is water essential for Life to exist on Earth. The cohesive properties of water cause the molecules on the surface of water to be drawn inward which is why drops of water form beads on a smooth surface. Cohesion also explains why some insects and spiders can walk on a ponds surface.
Water the liquid commonly used for cleaning has a property called surface tension. Start studying Biology - Properties of Water. Cohesion is the property of water that refers to water molecules sticking to each other.
What is so important. Water is highly cohesive and adhesive. We are about 60 water - and there are some organisms that are as much as 90 water.
This means that wherever water goes either through the ground or through our bodies it takes along valuable chemicals minerals and nutrients. Water has a high specific heat capacity specific heat capacity amount of energy required to raise temperature of 1 g of water by 1C 1 calorie 1 cal Large bodies of water stabilize the air temperature. The cohesive forces between water molecules are responsible for the phenomenon known as surface tension.
Properties Of Water A Biology PROPERTIES OF WATER Thermal Properties Large amounts of energy are needed to break the hydrogen bonds. This four minute animation describes the properties of water that support life. Ionic and Covalent bonds.
Adhesion is the property of water that refers to water molecules sticking to another surface. In the body of the water each molecule is surrounded and attracted by other water molecules. Start studying Properties of Water- Biology.
Indeed water as found in nature almost. 0201 Properties of Water Key Questions and Terms Notes What is the chemical formula for water. 5 properties of water.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Unlock the full A-level Biology course at httpbitly2togNBT created by Adam Tildesley Biology expert at. Cohesion high specific heat high heat of vaporization lower density of ice and high polarity.
This means that water warms and cools slowly. Atoms that are ionically bonded together form an ionic compound. It is in this simplicity and the polar nature of the molecule that makes water such an amazing substance.
Water has some unusual properties due to its hydrogen bonds. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. This allows it to be the solvent of life.
Adhesion is an important property. 163 The Properties of Water. Water is called the universal solvent because it dissolves more substances than any other liquid.
Physical Properties of Water The physical properties of water differ markedly from those of other solvents. Two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom make up the whole of the molecule. Because of hydrogen bonds water molecules develop strong intermolecular attraction between them.
One property is cohesion the tendency for water molecules to stick together. The Four Emergent Properties of Water Shem Johnson Biology 1610025 The water molecule by appearance doesnt look like much. These properties include solvency cohesion and adhesion high surface temper.
This is called cohesion. Because organisms have a high water content a large amount of energy only results in a small increase in body temp. Both of these properties are due to hydrogen bonding and how hydrogen bonding orients the water molecules.